Example topology
Cisco Nexus VPC – best practices
vpc domain 1 peer-gateway peer-switch ip arp synchronize delay restore 120 graceful consistency-check auto-recovery auto-recovery reload-delay 240
If configuring “peer-switch” vPC vlans priority on both switch must be the same !!!
Use the command spanning-tree vlan <vPC vlans> priority <priority> on both switches
Recommendations
1. vPC domain id must be different on both layers because this
information is used as part of the LACP protocol. Using the same vPC domain id will generate continuous
flaps on vPC interconnecting the NEXUS 5000 to NEXUS 7000.
If user absolutely wants to use the same domain-id on both vPC domains, then knob system-mac(under vPC domain configuration context) must be used to force different vPC system-mac values.
vPC system-mac and vPC local system-mac are both used in the LACP protocol as the LACP system ID
2. Spanning tree ports configuration
3. LACP mode active-active (on both sides of the port-channel) is the recommended configuration
4. If the downstream access switch is a not a Cisco Nexus device, disable the LACP graceful-convergence option.
5. vPC ports limitations:
• PIM SM (Sparse Mode) is fully interoperable with vPC. The software does not support PIM BiDIR or PIM SSM (Source Specific Multicast) with vPC.
• The software does not support DAI (Dynamic ARP Inspection) or IPSG (IP Source Guard) in a vPC environment.
• DHCP relay and DHCP snooping are supported with vPC.
• The software does not support Cisco Fabric Services regions with vPC.
• Port security is not supported on vPC member ports.
6. Any vPC VLAN allowed on vPC member port MUST be allowed on vPC peer-link.
7. Use show vpc orphan-ports command to display all Orphan Ports on vPC peer device
8. Use same vPC ID as port-channel ID for ease ofconfiguration, monitoring, and troubleshooting
9. Configure a separate Layer 3 link for routing from the vPC peer device (backup routing path), rather than using vPC peer-link and SVI for this purpose.
10. Bridge Assurance
• Let Bridge Assurance running on vPC peer-link (default mode) and do not disable it.
• Do not use bridge assurance command for interconnect remote sites
• Do not enable Bridge Assurance on vPC member ports.
11. Create an additional Layer 2 trunk port-channel to transport non-vPC VLAN traffic(if doing so, make sure that the VLANs are not in the same MST group).
12. Use MST with vPC if you need to build a large L2 domain
13. When using vPC, it is a best practice to use default timers for HSRP, VRRP and PIM configurations.
14. vPC peer-keepalive:
• Do not configure vPC peer-keepalive link on top of vPC peer-link!!
• Use Mgmt0 interface for vPC peer-keepalive
• Do not connect mgmt0 ports in back-to-back mode across the two switches
15. vPC peer-link
• Use at least 2 different line cards to increase high availability of peer-link.
• Use dedicated 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports with M132 10G line card. Do not use shared mode ports.
• Do not insert any device between vPC peers. A peer-link is a point-to-point link
• It is mandatory that both sides of vPC peer-link are strictly identical (M1 to M1, F1 to F1, F2 to F2..)
• ports on M132XP can used for vPC peer-link only if the port is configured in dedicated mode.
• For vPC peer device with a only one M1 line card use vPC object tracking feature.
16. vPC peer-gateway
• Always enable vPC peer-gateway in the vPC domain
Use the command peer-gateway under VPC domain to allow both N7K forward traffic of each other HSRP
(even if destination MAC is of the other N7K)
• If you configure a VLAN for OSPF over the vPC, you must exclude that vlan from peer-gateway, use the command – peer-gateway exclude-vlan .
17. vPC Peer-switch
• Configure the command peer-switch under vpc domain
• When vPC peer-swtich is activated, both vPC peer devices MUST have the same spanning tree configuration, same Spanning Tree Protocol priority for all vPC VLAN
18. vPC ARP Sync
• Always enable vPC ARP Sync on both vPC peer devices.
Use the command – ip arp synchronize under vpc domain
19. vPC delay restore
• Always enable vPC delay restore (on both vPC peer devices) and the tune the timer accordingly based on network profile.
Use the command – delay restore under vpc domain
20. vPC graceful type-1 check
• Always enable vPC graceful type-1 check on both vPC peer devices.
Use the command – graceful consistency-check under vpc domain (enabled by default)
21. vPC auto-recovery
• Always enable vPC auto-recovery on both vPC peer devices
Use the command – auto-recovery under vpc domain
22. vPC auto-recovery reload-delay
• Always enable vPC auto-recovery reload-delay on both vPC peer devices.
Use the command – auto-recovery reload-delay under vpc domain
23. When connecting a Cisco Nexus device to a Cisco Catalyst device, be cautious with the VLAN used for that purpose in order to avoid any reserved VLANs from the NX-OS range or IOS range.
(IOS reserve vlans 1006-1018, NX-OS reserve vlans 3968-4094)
24. Attaching a L3 device (router or firewall configured in routed mode for instance) to vPC domain using a vPC is not
a supported design because of vPC loop avoidance rule.
(Need to connect with ECMP L3 links)
25. Enable Layer 3 connectivity between vPC peer device by configuring a VLAN network interface for the
same VLAN from both devices or by using a dedicated L3 link between the 2 peer devices (for L3 backup
routing path purposes).
Good to know
General
A Layer 2 port-channel only is supported with vPC (no Layer 3)
vPC Data-Plane Loop Avoidance
vPC performs loop avoidance at data-plane layer instead of control plane layer for Spanning Tree Protocol.
All logics are implemented directly in hardware on vPC peer-link ports, avoiding any dependancy to CPU utilization.
vPC peer devices always forward traffic locally when possible,
vPC loop avoidance rule states that traffic coming from vPC member port, then crossing vPC peer-link is NOT
allowed to egress any vPC member port; however it can egress any other type of port (L3 port, orphan port, …).
vPC Role
(primary / secondary)
vPC role defines which of the two vPC peer devices processes Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) and responds to Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
When vPC peer-link is down, The secondary peer device shut down vPC member ports.
CFS
Cisco Fabric Services (CFS) protocol performs the following functions:
● Configuration validation and comparison (consistency check)
● Synchronization of MAC addresses for vPC member ports
● vPC member port status advertisement
● Spanning Tree Protocol management
● Synchronization of HSRP and IGMP snooping
Cisco Fabric Services is enabled by default when vPC feature is turned on.
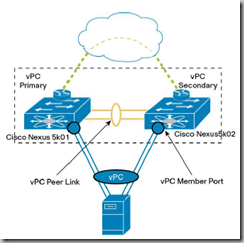
vPC Peer-Link
The vPC peer-link is a standard 802.1Q trunk that can perform the following actions:
● Carry vPC and non-vPC VLANs.
● Carry Cisco Fabric Services messages that are tagged with CoS=4 for reliable communication.
● Carry flooded traffic from the other vPC peer device.
● Carry STP BPDUs, HSRP hello messages, and IGMP updates.
vPC peer-link is supported on all shipping 10G line card. It is not supported on any 1G line card nor on any FEX
ports (including the 2232 model which has 10G front panel ports).
vPC peer-gateway
allow both N7K forward traffic of each other
a knob is available to exclude specific VLANs from the peer-gateway.
These VLANs are typically used for backup routing paths. The command is:
N7k(config-vpc-domain)# peer-gateway exclude-vlan
vPC Peer-Switch
The vPC Peer-Switch feature (Figure 42) allows a pair of vPC peer devices to appear as a single Spanning Tree
Protocol root in the Layer 2 topology (they have the same bridge ID). vPC peer-switch must be configured on both
vPC peer devices to become operational. The command is the following:
N7K(config-vpc-domain)# peer-switch
HSRP/VRRP active/active with vPC
HSRP and VRRP operate in active-active mode from data plane standpoint (by default), as opposed to classical active/standby
implementation with STP based network.
HSRP/VRRP – Active/Active/Active (core and DR sites)
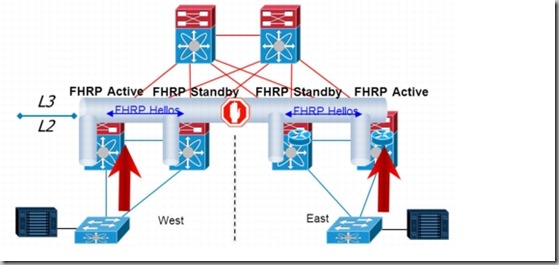
PACL configuration to stop HSRPv1 hello messages:
ip access-list HSRPv1_Filtering 10 deny udp any 224.0.0.2/32 eq 1985 20 permit ip any any
PACL configuration to stop HSRPv2 hello messages:
ip access-list HSRPv2_Filtering 10 deny udp any 224.0.0.102/32 eq 1985 20 permit ip any any
PACL configuration to stop VRRP hello messages:
ip access-list VRRP_Filtering 10 deny udp any 224.0.0.18/32 eq 1985 20 permit ip any any
To apply the PACL to DCI vPC link, apply the PACL on each member ports (example with HSRPv1):
Interface Po10 ip port access-group HSRPv1_Filtering
Thanks Sharon …. looks like a useful stuff, will ponder through it & comment on it in case I have any questions.
Great article, thank you very much for the additional configuration parameters as it concerns vpc tuning and application…